- Points To Remember
- Gross Income vs. Net Income: Definition
- What Is Gross Income?
- Revenue
- Cost Of Goods Sold
- What Is Net Income?
- Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Calculation
- Gross profit
- Net Profit
- Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Key Differences
- Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Limitations
- Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Users
- Business Owners And Management
- Investors
- Lenders And Banks
- Tax Authorities
- Concluding
Gross Income Vs Net Income – Find Out The Differences And Methods For Calculating

Gross income and net income are the two vital profitability metrics for any business. Gross income represents the income that remains with the business after deducting the cost of production from the revenue. The amount generated from the sales of the goods and services of a company is its revenue. Let’s Find Out About Gross Income Vs Net Income.
Gross income is a determining factor that helps stakeholders find out the company’s earnings from production and sales. Gross income is also known as gross profit.
In contrast, net income is the profit businesses are left with after deducting costs and expenses from the revenue. Net income is also known as net profit. it helps investors determine if the company is profitable. And, if not, what are the areas where its bearing loss.
Points To Remember

- Gross income is the profit of a company calculated after deducting the production and distribution costs from the total revenue.
- Gross profit is a determinant factor of a company’s capability to produce profit while keeping up with production and labor costs.
- Net income is the profit that is calculated after all the expenses have been deducted from the revenue.
- Net profit is an all-inclusive metric for profit generation and gives insights into how efficiently the management manages all the business aspects.
- In a financial statement, net income is referred to as the bottom line.
Gross Income vs. Net Income: Definition
The fundamental difference between what net income and what gross income mean are:
What Is Gross Income?

The profit earned by a company after deducting the production and selling costs- called the cost of goods sold (COGS) from its total revenue is known as the gross income. Also known as gross profit, it gives insights into how effectively a business is managing its production costs that, which include labor and supply costs,
The two main components while calculating the gross income are:
Revenue

Revenue is the total amount that is generated from the sales of the products or services of a company during a given time. This time frame does not necessarily have to be a full financial year; it can be half-yearly or quarterly.
Revenue is also known as net sales, as it is inclusive of all the discounts and deductions from damaged or returned products.
The amount representing the returned goods is subtracted from the revenue to get the actual revenue earned. Revenue is also called a “top line” number because it is written at the top of the income statement.
Cost Of Goods Sold
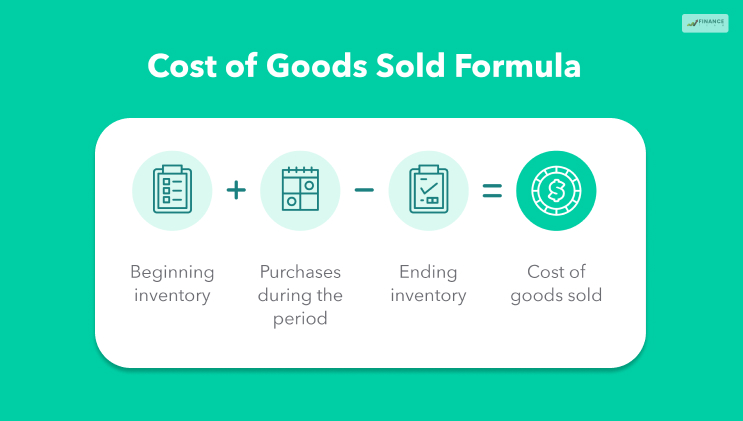
This refers to the direct costs that are involved in producing the goods that are sold by a company. They may include:
- Raw materials and inventory
- Production labor wages
- Equipment cost
- Repair cost
- Shipping cost
- Utilities for production facilities
What Is Net Income?

It is the same as the company’s profit during one accounting period. This means net profit includes all costs and expenses that are incurred by a company that is subtracted from its revenue.
A company may add multiple items to the statement; the net profit is usually calculated by deducting the following expenses:
- Operating expenses
- Interest on debts and loans
- Selling, general, and administrative expenses
- Income tax
- Depreciation
Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Calculation
The steps to calculate both income methods are as follows:
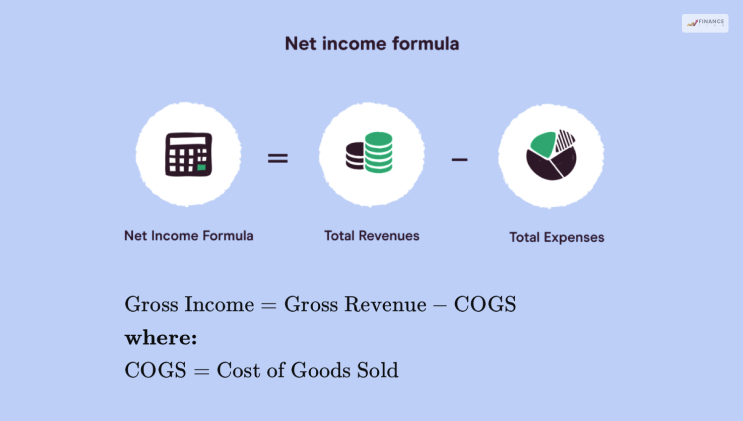
Gross profit
Gross Income = Revenue – COGS[cost of goods sold]
Net Profit
Net Profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
To simplify it further,
Net Profit = Gross income – Operation Expenses – Other Expenses – Taxes – Debt Interest + Other Income
Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Key Differences

Gross profit evaluates the ability of a company to generate profit alongside managing its production and labor costs. Hence, it is an important metric that helps in deciding upon the reasons why a company’s profit is going up or down, looking at the sales, labor costs, production costs, and productivity.
When a company reports increased revenue, but it is more than redeemable in production costs, the gross income will be low for that period.
For example, due to a busy season, if the company is not able to hire enough production laborers, that would lead them to overtime pay for the existing workers. That will result in higher labor costs and depletion of gross profit. However, gross income cannot be the only profitability metric for a company as it does not include all the other compulsory expenses that are necessary to run a business.
In comparison, net profit represents the profit from every single aspect of a company’s operations. Hence it makes net profit more inclusive and provides an insight into how effectively the management is performing.
For example, if a company is increasing its gross profit by borrowing from the market, the additional interest expense for debt will reduce the net profit in spite of the company making successful sales and production.
Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Limitations

Both gross income vs net income have some limitations of their own. Whereas gross income is not a very effective metric by itself, net profit is far more helpful in deciding the financial position of a company.
But at the same time, net profit is also limited as it can only be used to calculate the performance of a company from one year to the other.
Even comparing the net profits of two different companies doesn’t tell you a lot about the companies either, despite being in the same industry.
Net profit can also be misleading as non-cash expenses are not inclusive of its calculation. A drastic change in the net income can be noticed when these deductions are made.
Gross Income Vs. Net Income: Users
In most cases, the basic difference between gross income vs net income is the different user preferences depending on their need for information.
Business Owners And Management

While gross profit is used by the management to get information about the profitability of the core business, the net income is more detailed and gives more specific information about the profit. If the managers need to know what the net income is after taxes, they will look into the net income and not the gross income.
Investors

Investors are more interested in knowing the net profit than the gross profit as it helps them understand the potential RoI that the company can bring.
Lenders And Banks

Because the gross income for companies is mostly positive, banks and other financial institutions take a look at the net profit of the company before making lending decisions.
Tax Authorities

All the taxes that include federal, state, and local taxes are based on the net profit. There are very small marginal deductions that depend on gross profit; the government is more interested in the net profit while evaluating tax.
Concluding
Although the net income is far more valuable than the gross income, it is impossible to run a successful business if you choose to only value anyone between gross income vs. net income. Both gross incomes vs. net have their own purposes and importance that they serve, and both must be evaluated effectively for any business to grow.
Read Also:
- What Is Zero-Based Budgeting? | Benefits, Process and Examples
- How To Find Marginal Cost? Why Is It Important For Businesses?
- How To Calculate Opportunity Cost? And What Is Its Use?










